          |
|
“Fluid” solve Navier-Stokes equations for incompressible, viscous fluid on Euler grid. It’s use also Poisson equation to solve pressure. Mass conservation condition. 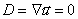 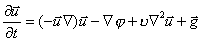 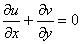 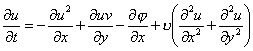 Where: 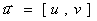 - local velocity vector - local velocity vector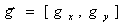 - gravity vector - gravity vector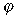 - pressure to density ratio - pressure to density ratio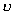 - viscosity - viscosityWe are solving two dimensional equations in cartesian coordinates [i x j]. There is 2D grid with NX*NY cells (from 1...i..NX, 1...j...NY). 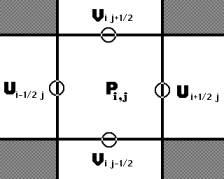 Representation on a euler grid. Representation on a euler grid. Local velocitien on edge of cells. Pressure to density ratio inside of fluid. There is also other of values inside of cell, but that are most important. 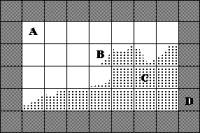 Types of cells. Types of cells.Every cells are flagged: A – boundary cell (slip or noslip) B – empty cell C – surface cell D – full of fluid For representation of fluid surface i’m using markers. Its very interesting method called THE MAC METHOD. Markers are mass-less. Markers dont get use in numerical calculations, they are used only for show actual configuration of fluid on a grid and to type surface cells. Velocities of markers (they are moving every time step) im get from a grid with interpolation of local velocities in cell. |